Congress is one of the biggest political parties in India. It is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or some other groups. It is being run by several well-known ministers such as Rahul Gandhi, Mallikarjun Kharge, Sonia Gandhi, and more. Have you ever wondered why this party is called Congress. Do you know the meeting of this world, if not so here we have shared some information that you should know.
Table of Contents

What Is Congress?
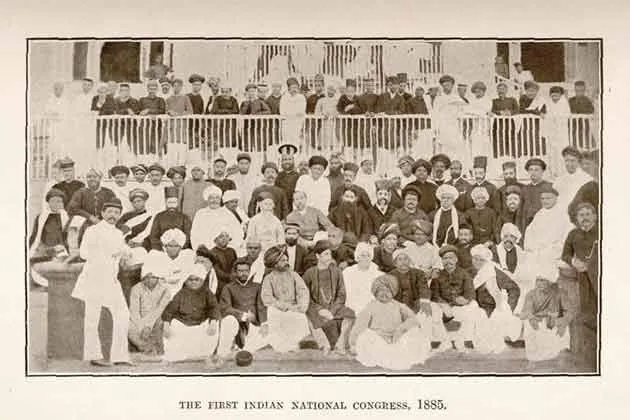
Congress is an Indian political party, it is also known as the Indian National Congress (IC) or the Congress Party. This political party is deeply rooted in most of the regions of India such as Gujrat, Delhi, and more. It was officially founded on 28th December 1885 and it is the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Empire in Africa and Asia.
Since the 19th century, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, the Indian National Congress became the principal leader of the Indian Independence movement. The party led India to independence from the UK and influenced other anti-colonial nationalist movements in the British Empire.
Why It Is Called Congress?
Congress stands for the act or action of coming together and meeting. The Congress party was formed in 1885 and it dominated the Indian movement for independence from Great Britain. It was first officially convened in December 1885. Because of the idea of a nationalist movement opposed to British rule dated from the 1850s. During the time of the first several decades, the Congress Party passed moderate reform resolutions through the organization.
The retired British Indian Civil Service officer Allan Octavian Hume founded the Indian National Congress. he founded this political party to form a platform for the civil and political dialogue among educated Indians. The control of India was shifted from the East India Company to the British Empire after the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Congress was established when a total of 72 representatives from the entire nation met at Mumbai (formerly known as Bombay) in 1885. The list of prominent delegates includes Dadabhai Naoroji, Badruddin Tyabji, Surendranath Banerjee, Pherozeshah Mehta, W.C. Banerjee, S. Ramaswami Mudliar, Romesh Chunder Dutt, and S. Subramania Iyer. Also, one of the founding members of INC was the Englishman Allan Octavian Hume who was a former British civil servant.
Foundation Of Congress
The Englishman Allan Octavian Hume, a retired British civil servant who was also recognized for his pro-Indian activities thought of an idea for a body that could represent Indian interests in the open letter to graduates of the University of Calcutta. The main target was to obtain a greater share in the government for the educated Indians and also to create a platform for the civic and political dialogue between them and the British Raj.
Hume organized the first meeting in Bombay with the approval of Umesh Chandra Banerjee and Viceroy Lord Differin was the present of Congress. The first official session was attended by 72 delegates who represented each province of India. The unrepresentative of the Indian masses at the time functioned over the stage for elite Indian ambitions rather than a political party for the first two decades of its existence because most of the Congres’s founding members were educated or lived in British.
Jawaharlal Nehru Contribution To Congress
Jawaharlal Nehru made a very big contribution to the Congress party. From 1951 till his last breath, he dominated the Congress party, which won overwhelming victories in the elections of 1951-52, 1957, and 1962. This party united in 1964 to elect Lal Bahadul Shastri and then in 1966 Indira Gandhi who was the daughter of Nehru, to the posts of party leader and prime minister.
Indira Gandhi is known for her great leadership and she is also known as the best minister that India has ever seen. She faced a clear open revolt within the party and then after 2 years, she was expelled from the party by a group known as Syndicate. Till now she is recognized as the most powerful politician who helped India in growth.
Early Years Of Indian National Congress
Two factors emerged with the party and led to several different approaches and ideologies that are related to the methods to gain self-rule for India. There was a division that arose among the Moderates, it was led by Gopal Krishna Gokhale who used to believe in peace and a constitutional approach to gain reforms and also self-governance within the framework of the British Empire.
Mahatma Gandhi In Congress
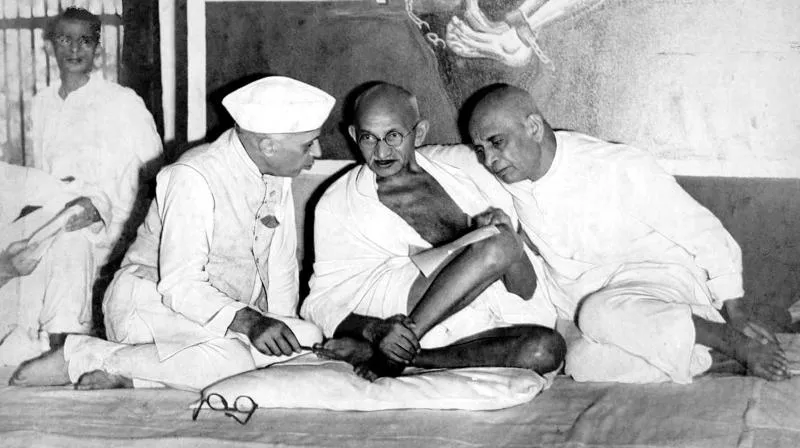

They targeted to collaborate with the British authorities and also used constitutional resolutions, dialogue, and petitions to address the grievances of Indians. When Mahatma Gandhi again returned to India from South Africa in 1915, he joined Congress. So between 1917 and 1918, he was involved in three struggles, recognized as the Ahmedabad Mill Strike, Kheda Satyagraha, and Champaran Satyagraha.
When World War 1 got finished then the party came to be associated with him who just remained its unofficial spiritual leader and icon. Gandhi allied with the Khilafat Movement in 1920 as part of his opposition to British rule in India. he fights for the rights of every single individual using civil disobedience as a tool for agitation. But he suspended the agitation in 1922 after the passing of policeman Chauri Chaura.
During the ending period of World War 2 in 1945, the Labour Party of the United Kingdom was the election to give independence to India. Then in the next year, the British tried to soldiers of Japanese Japanese-sponsored Indian National Army in the INA trials. So at that time, the Congress party helped the INA Defence Committee. It assembled the legal team to defend the case of the soldiers of the Azad Hind movement.
Congress Post-Independence
India got its independence in 1947, then the Congress Party became the dominant political party in the country. The first general election was officially held after independence in 1952. The part got turned to power in the national parliament and most state legislatures.